c++ notes:recall of move-semantics and rvalue-reference (2)
回顾:
G1-G4:
G1. If a variable or parameter is declared to have type T&& for some deduced type T, that variable or parameter is a universal reference.
G2.
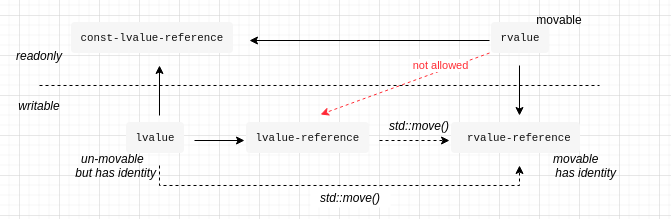
If you can take the address of an expression, the expression is an lvalue. If the type of an expression is an lvalue reference (e.g., T& or const T&, etc.), that expression is an lvalue. Otherwise, the expression is an rvalue. Conceptually (and typically also in fact), rvalues correspond to temporary objects, such as those returned from functions or created through implicit type conversions. Most literal values are also rvalues.
G3.
- If the expression initializing a universal reference is an lvalue, the universal reference becomes an lvalue reference.
- If the expression initializing the universal reference is an rvalue, the universal reference becomes an rvalue reference.
G4. Deduce Rules: T& && => T& T&& & => T& T& & => T& T&& && => T&&
本文内容涉及:移动语义/右值引用.
右值引用
lvalue to rvalue
- 右值引用设计目的:从即将销毁的元素偷取资源,以此来避免拷贝。
- 移动语义:
- 元素的构造函数&赋值操作符的入参增加右值引用,表示从某个即将被摧毁的元素获取某些资源。
- “rule of five”: 相对于"rule of three"增加移动构造函数和移动赋值操作符。
移动语义关键词
- “rule of five”
- “steal resource”
- a rvalue is something that is about to be destoryed.
std::movedo not modify life time of a var, but make it movable.
值类别(value categories)
VALUE CATEGORIES
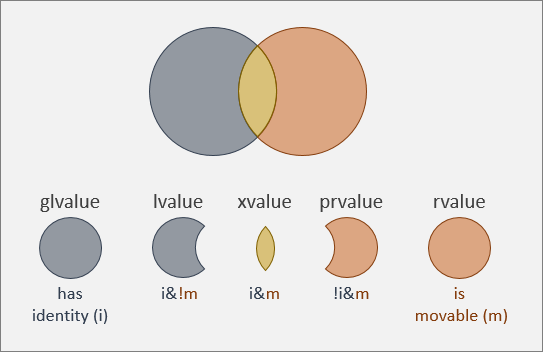
lvalue - 左值,具名且不可移动
xvalue - 将亡值, 具名可移动,即将被销毁的值 (其实感觉上右值引用就是xvalue) 。如:std::move产生出来的值…
glvalue - 泛左值,具名.
prvalue - 纯右值,可移动不具名.
rvalue - 右值,可移动.

